Part A: Survey of mobile device capability and Web 2.0 tools
What is Web 2.0?
First of all, we need to have an idea of what Web 2.0 is about. It has been a very hot topic in the Internet world. At this stage, Web 2.0 is still very cloudy and many people (including researchers, developers and users) are having different interpretations on it. I have actually read through a few comtemporary research arcticles and can only give a very general summary based on the majority views.
Without doubt, Web 2.0 encourages interaction and collaborative work through the Internet no matter you are a developer or an user. Nowadays, many popular websites such as FaceBook, Google Maps and My Space are operating according to this concept (O'Reilly 2005). Social networking is one of the outcomes of Web 2.0. From the perspective of developers, web becomes the development platform by which applications the services are delivered (Pilgrim 2008).
Wigand, Benjamin & Birkland (2008) claims that '...Web 2.0 is a paradigm shift how users use the web, a development that questions everything that has been developed and applied so far. Pilgrim (2008) also agrees with the shift in the paradigm of users' behaviour. In addition, he criticises that the rush to embrace Web 2.0 has resulted in many developers overlooking principles of good design and usability established over the last decade. This is an imperative issue for designing OTBS with the concept of web 2.0 but shouldn't go beyond the pre-defined scope.
1.Find out and recommend what type of mobile devices are suitable for:Just the SMS message service;
a.Just the SMS message service;
I have reviewed a few taxi-booking systems in the major cities such as Perth, Ho Chi Minh City, Sinagaporeb and etc. This is practical and economically and technically feasiable to use the SMS message service the OTBS. In the market, there are many taxi booking systems are available and they employs SMS as one of the communication means between the passengers and the service centre.
b.The full user experience via SMS, GPS Taxi tracking and Google Maps
In Ho Chi Minh City, the taxi booking system, DiaDiem integrates the global positioning system (GPS) and touch screen devices inside a vehicle with the ability to communicate with a mobile phone or website. It focuses on three different perspectives: the customer, call center and taxi.The customer will first use a website, a mobile application or an SMS message to place a taxi pickup order. The website will be launched by DiaDiem later. The order placing process is conducted with the support of a DiaDiem software via a transmission medium (SMS, GPRS or Wi-Fi)( TN 2009).
2.Describe any new hardware, networking, software, systems, procedures and personnel that would be needed by the taxi company Website to support this stage 2 development.
Hardware: touch screen devices with GPS in each taxi, Cell phone or wireless devices with GPRS or 3G that can browse Google map
Software: OTBS backend server and WebSMS software used by the service centre; and Google map used by both passengers and drivers
Networking and system: SMS system including WebSMS, GPS system for GPS tracking
Implementation/Training: cost incured on the implementation and training
Part B: The enhanced customer experience through Web 2.0 technology
1.Use a table to describe how the customer experience is improved by:
a.Horizontal scalability (eg ordering a taxi by mobile phone call or SMS, mobile Internet, desktop or laptop computer)
b.Service oriented features (eg SMS updates using location data, knowing the driver’s name before the ride and being greeted by your name etc)
c.Other customer services enabled by Web 2.0 (eg reputation system)
 Part C: Online Taxi Business Process Modelling
Part C: Online Taxi Business Process Modelling
Apart from the business basics of offering a clean car, safe driving, being on time, consider the business processes involved and construct a Simple Online Taxi business process model using any suitable drawing tool.
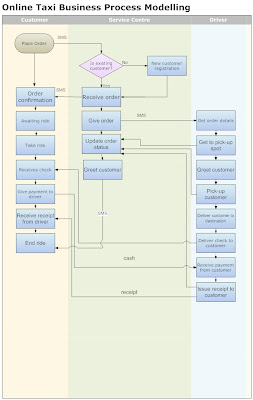
References
O'Reilly, T 2005, What Is Web 2.0:Design Patterns and Business Models for the Next Generation of Software, O'Reilly Media, Inc, viewed 27 May 2009,
<http://www.oreillynet.com/pub/a/oreilly/tim/news/2005/09/30/what-is-web-20.html>.
Pilgrim, JC 2008, 'Improving the usability of web 2.0 applications', Conference on Hypertext and Hypermedia:Proceedings of the nineteenth ACM conference on Hypertext and hypermedia, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, pp. 239-240, <http://delivery.acm.org/10.1145/1380000/1379144/p239-pilgrim.pdf?key1=1379144&key2=9831173421&coll=GUIDE&dl=GUIDE&CFID=38231369&CFTOKEN=10579826>.
TN 2009, First GPS Integrated Taxi booking system to debut, Vietnam Business Finance, posted 27 April, viewed 6 June 2009, <http://www.vnbusinessnews.com/2009/04/first-gps-integrated-taxi-booking.html>.
Wigand, TR, Benjamin, IR & Birkland, LHJ 2008, 'Web 2.0 and beyond: implications for electronic commerce', ACM International Conference Proceeding Series: Proceedings of the 10th international conference on Electronic commerce, Innsbruck, Austria, vol 342, article 7, also available in pdf format, <http://delivery.acm.org/10.1145/1410000/1409550/a7-wigand.pdf?key1=1409550&key2=9823863421&coll=GUIDE&dl=GUIDE&CFID=38172456&CFTOKEN=67009489>.
Zajicek, M 2007, 'Web 2.0: Hype or Happiness?', ACM International Conference Proceeding Series:Proceedings of the 2007 international cross-disciplinary conference on Web accessibility (W4A), Banff, Canada, vol 225 pp. 35-39, <http://www.w4a.info/2007/prog/k2-zajicek.pdf>.




No comments:
Post a Comment